Voltage Regulators and Power Supplies » Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulators » S13VxFx Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulators »
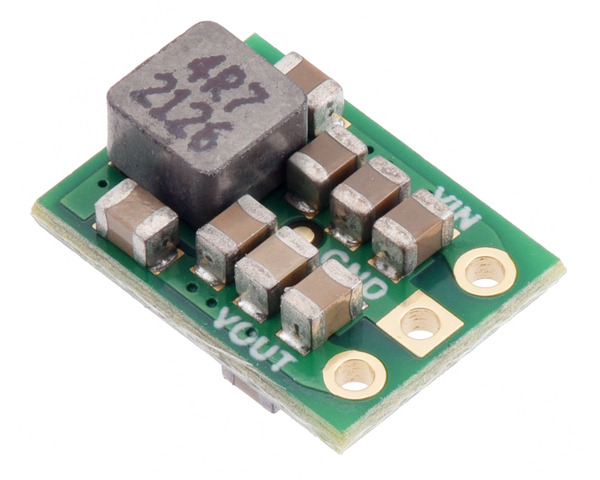
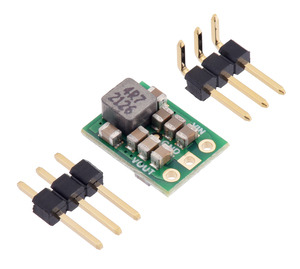
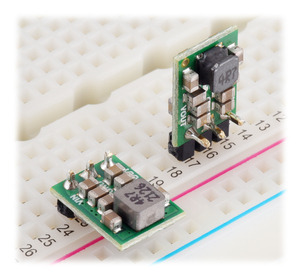
5V, 2A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V20F5
| Output voltage | Typical max output current* |
Input voltage range | Size | Optional enable input |
Reverse voltage protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
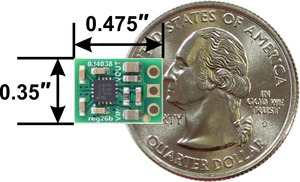
| 5 V | 2 A | 2.8 V – 22 V | 0.35″ × 0.475″ | – | – |
*For input voltages close to the output. Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product page for more information.
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): continuous output current Select variant…
 Compare all products in S13VxFx Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulators.
Compare all products in S13VxFx Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulators.
| Description | Specs (11) | Pictures (13) | Resources (3) | FAQs (0) | On the blog (2) | Distributors (55) |
|---|
Overview
 |
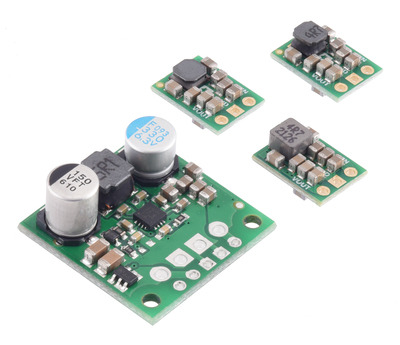
The S13VxF5 family of efficient switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) use a buck-boost topology to convert both higher and lower input voltages to a regulated 5 V output. They take input voltages from 2.8 V to 22 V and increase or decrease them as necessary, offering a typical efficiency of over 85% and typical continuous output currents between 1 A and 3 A . The flexibility in input voltage offered by this family of regulators is especially well-suited for battery-powered applications in which the battery voltage begins above 5 V and drops below as the battery discharges. Without the typical restriction on the battery voltage staying above the required voltage throughout its life, new battery packs and form factors can be considered.
This family consists of the S13V30F5, which is a larger (0.9″ × 0.9″) high-current version:
and three extra-compact (0.35″ × 0.475″) lower-current versions:
- S13V10F5: 1 A continuous output current
- S13V15F5: 1.5 A continuous output current
- S13V20F5: 2 A continuous output current
The regulators have under-voltage lockout, output over-voltage protection, and over-current protection. A thermal shutdown feature also helps prevent damage from overheating and a soft-start feature limits the inrush current and gradually ramps the output voltage on startup. The larger 3 A S13V30F5 has reverse-voltage protection up to 20 V, but the S13V10F5, S13V15F5, and S13V20F5 do not.
 |
The extended S13VxFx family also includes versions with other output voltages
 |
3.3V Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V25F3. |
|---|
The S13V25Fx family, which is pin-compatible with the S13V30F5, consists of six 2.5 A regulators with output voltages ranging from 3.3 V to 15 V:
- S13V25F3: 3.3V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
- S13V25F6: 6V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
- S13V25F7: 7.5V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
- S13V25F9: 9V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
- S13V25F12: 12V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
- S13V25F15: 15V output with 2.5 A continuous output current
These versions have the same overall board dimensions as the S13V30F5, but please note that the tall components (i.e. electrolytic capacitors and inductor) are in different locations.
Details for item #4085
|
|
Note: This product is the 5V, 2A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V20F5. It can be distinguished from the similar-looking S13V10F5 and S13V15F5 by the inductor style, which is different for each of the three versions, and by the “reg26c” and “0J4039” markings on the PCB silkscreen (see the right picture above).
Features
- Input voltage: 2.8 V to 22 V
- Output voltage: 5 V with 3% accuracy
- Typical maximum continuous output current: 1 A to 2.5 A, depending on input voltage (see the maximum continuous output current graph below)
- Typical efficiency of 85% to 95%, depending on input voltage and load (see the efficiency graph below)
- 10 mA to 20 mA typical no-load quiescent current (see the quiescent current graph below)
- Input under-voltage lockout and output over-voltage protection
- Soft-start feature limits inrush current and gradually ramps output voltage
- Over-current protection and over-temperature shutoff
- 5 A output current limit
- Fixed switching frequency of ~500 kHz
- Double-sided assembly for extra-compact size: 0.35″ × 0.475″ × 0.22″ (8.9 mm × 12.1 mm × 5.6 mm); see the dimension diagram (720k pdf) for more information
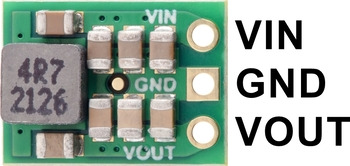 |
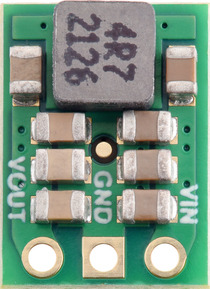
5V, 2A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V20F5 pinout. |
|---|
Connections
The step-up/step-down regulator has just three connections: the input voltage (VIN), ground (GND), and the output voltage (VOUT). The input voltage, VIN, powers the regulator. Voltages between 2.8 V and 22 V can be applied to VIN. VOUT is the regulated output voltage.These through-holes are arranged with a 0.1″ spacing along the edge of the board for compatibility with standard solderless breadboards and perfboards and connectors that use a 0.1″ grid. A 3×1 straight male header strip and a 3×1 right-angle male header strip are included, and you can solder in the one that gives you your desired board orientation. Alternatively, you can solder wires directly to the board for the most compact installations.
|
|
Typical efficiency
The efficiency of a voltage regulator, defined as (Power out)/(Power in), is an important measure of its performance, especially when battery life or heat are concerns.
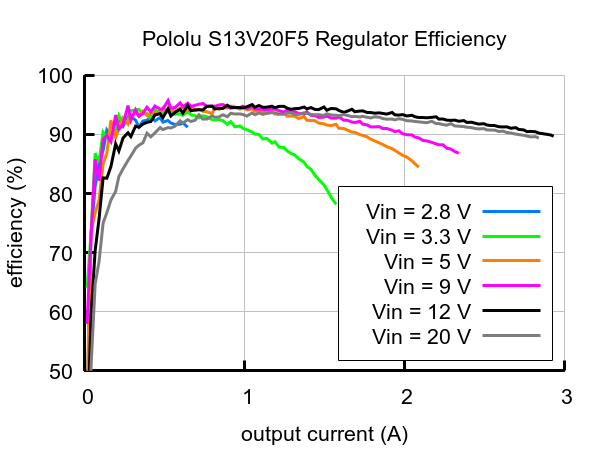 |
Maximum continuous output current
The maximum achievable output current of the regulator varies with the input voltage but also depends on other factors, including the ambient temperature, air flow, and heat sinking. The graph below shows maximum output currents that the regulators in the S13VxF5 family can deliver continuously at room temperature in still air and without additional heat sinking.
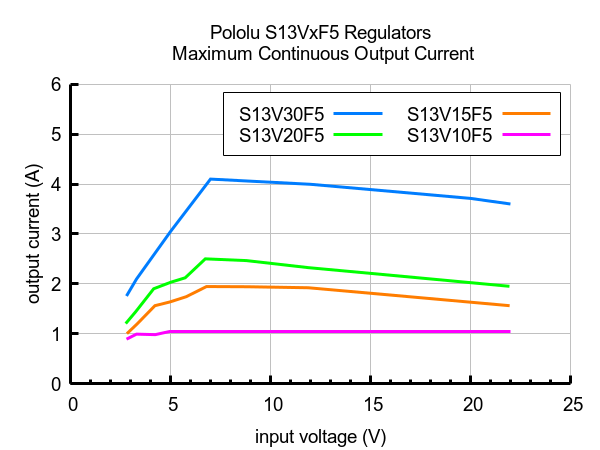 |
During normal operation, this product can get hot enough to burn you. Take care when handling this product or other components connected to it.
Quiescent current
The quiescent current is the current the regulator uses just to power itself, and the graph below shows this as a function of the input voltage.
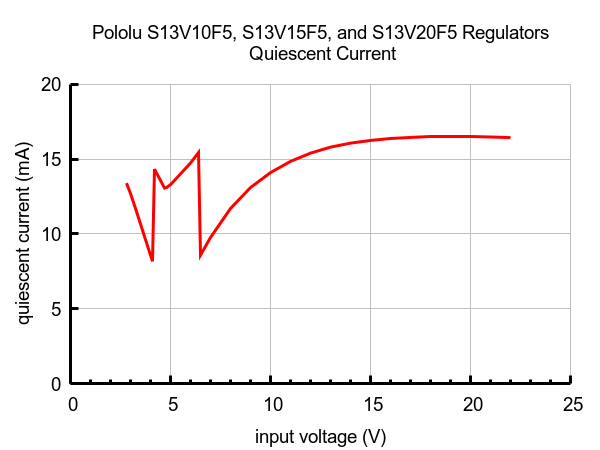 |
LC Voltage Spikes
When connecting voltage to electronic circuits, the initial rush of current can cause voltage spikes that are much higher than the input voltage. If these spikes exceed the regulator’s maximum voltage, the regulator can be destroyed. If you are connecting more than about 15 V, using power leads more than a few inches long, or using a power supply with high inductance, we recommend soldering a 33 μF or larger electrolytic capacitor close to the regulator between VIN and GND. The capacitor should be rated for at least 35 V.
More information about LC spikes can be found in our application note, Understanding Destructive LC Voltage Spikes.
People often buy this product together with:
 |
5V, 3A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V30F5 |
 |
5V, 1A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V10F5 |
 |
5V, 1.5A Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Regulator S13V15F5 |