Pololu Metal DC Gearmotors » 25D Metal Gearmotors » 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors »
4.4:1 Metal Gearmotor 25Dx63L mm LP 6V with 48 CPR Encoder
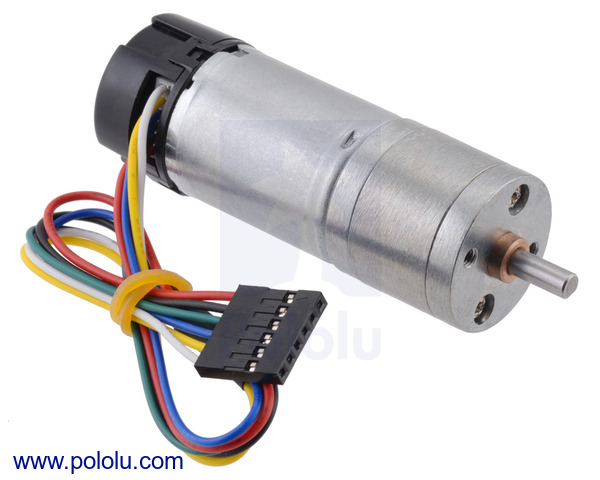
This gearmotor consists of a low-power, 6 V brushed DC motor combined with a 4.4:1 metal spur gearbox, and it has an integrated 48 CPR quadrature encoder on the motor shaft, which provides 211.2 counts per revolution of the gearbox’s output shaft. The gearmotor is cylindrical, with a diameter just under 25 mm, and the D-shaped output shaft is 4 mm in diameter and extends 12.5 mm from the face plate of the gearbox. This gearmotor is also available without an encoder.
Key specifications:
| voltage | no-load performance | stall extrapolation |
|---|---|---|
| 6 V | 1300 RPM, 120 mA | 0.63 kg⋅cm (8.7 oz⋅in), 2.0 A |
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): gear ratio motor type encoders? Select variant…
 Compare all products in 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors.
Compare all products in 6V Low-Power (LP) 25D mm Gearmotors.
| Description | Specs (17) | Pictures (11) | Resources (4) | FAQs (3) | On the blog (0) | Distributors (0) |
|---|
Dimensions
| Size: | 25D x 63L mm1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 95 g |
| Shaft diameter: | 4 mm2 |
General specifications
| Gear ratio: | 4.4:1 |
|---|---|
| No-load speed @ 6V: | 1300 rpm3 |
| No-load current @ 6V: | 0.12 A4 |
| Stall current @ 6V: | 2.0 A5 |
| Stall torque @ 6V: | 0.63 kg·cm5 |
| Max output power @ 6V: | 2.1 W |
| Motor type: | 6V, 2.0A stall (LP 6V) |
Performance at maximum efficiency
| Max efficiency @ 6V: | 49 % |
|---|---|
| Speed at max efficiency: | 1100 rpm |
| Torque at max efficiency: | 0.082 kg·cm |
| Current at max efficiency: | 0.32 A |
| Output power at max efficiency: | 0.94 W |
General specifications
| Lead length: | 8 in6 |
|---|---|
| Encoders?: | Y |
Notes:
- 1
- Length measurement is from gearbox face plate to back of encoder cap (it does not include the output shaft). See dimension diagram for details.
- 2
- D shaft.
- 3
- Typical; ±20%.
- 4
- Typical, ±50%; no-load current depends on internal friction, which is affected by many factors, including ambient temperature and duration of motor operation.
- 5
- Stalling is likely to damage the gearmotor. Stall parameters come from a theoretical extrapolation of performance at loads far from stall. As the motor heats up, as happens as it approaches an actual stall, the stall torque and current decrease.
- 6
- May vary by a few inches.