Pololu Blog »
New products: Motoron M2T256 (I²C) and M2U256 (UART) dual motor controllers
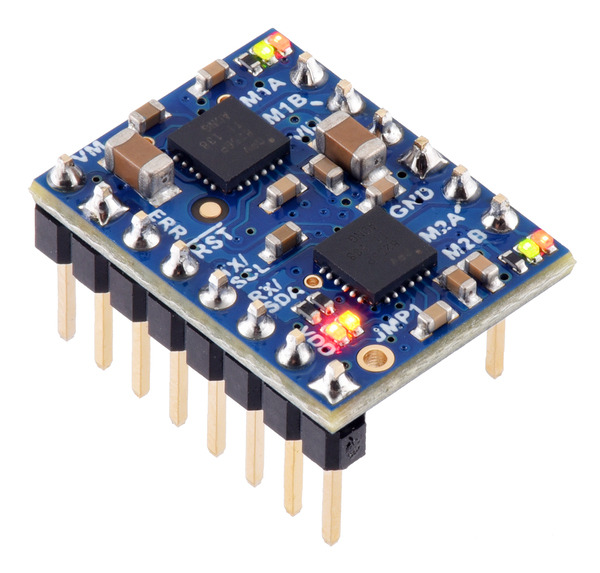
The Motoron family keeps growing! We’re happy to announce the release of the Motoron M2T256 Dual I²C Motor Controller and the Motoron M2U256 Dual Serial Motor Controller. Unlike previous Motoron controllers, these boards are “micro” versions that fit the ability to drive two motors (at up to 48 V and 1.8 A) into a minimal, compact form factor. They have the same ability to be individually addressed as the other Motorons, allowing many of them to be controlled independently while connected to the same bus.
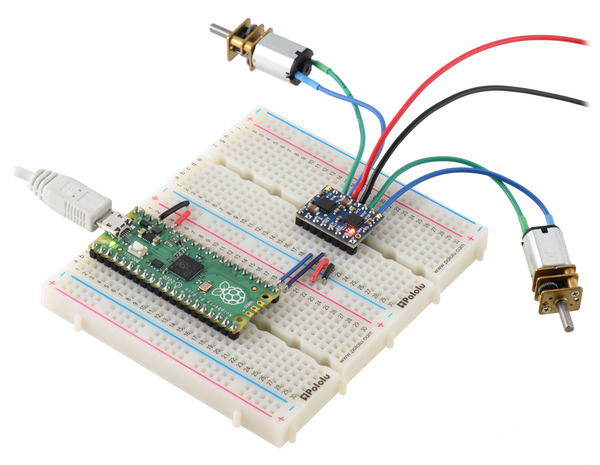 |
A Raspberry Pi Pico on a breadboard using a Motoron M2T256/M2U256 Dual Motor Controller to control two motors. |
|---|
The M2T256 is controlled via I²C like all of our previous Motorons, but unlike all the others, the M2U256 offers logic-level serial (UART) communication to provide an alternative option for applications where an asynchronous serial interface is preferred. The M2U256 supports the Pololu serial protocol, letting it share a serial line with our other compatible serial controllers (including brushed motor controllers, stepper motor controllers, and servo controllers). Its firmware also includes some options that can help you use it on an RS-485 network (requires addition of external transceivers).
The M2T256 and M2U256 both measure only 0.6″ × 0.8″ and have nearly the same pinout; in fact, both of these Motoron versions use the same printed circuit board with only minor differences in components. (For example, a resonator is only present on the M2U256 because it needs more accurate timing for asynchronous serial communication.) Both versions are available either with header pins soldered in or with headers included but not soldered.
|
|
The Motoron M2U256 is the latest in a succession of compact motor controllers we’ve produced over the years that use an asynchronous serial (UART) protocol, beginning with one of our very first products, the Pololu Dual Serial Motor Controller. Using this interface made a lot of sense in the past because it was one of the most straightforward ways to communicate with devices using higher-level commands. However, some of the most popular embedded platforms today make it difficult: many Arduino boards use the UART for serial programming, which can conflict with other connected devices, and a Raspberry Pi can output bootloader messages over serial or unexpectedly scale its UART frequency along with its CPU speed.
Meanwhile, I²C has become more popular and easier to use on microcontrollers over time, and it has features like open-drain lines and built-in support for addressing that simplify working with several devices on a single bus. This was the reason for the Motoron family’s initial focus on I²C, which was a departure from our tradition of making serial motor controllers, but the M2U256 reflects our thinking that there are still some reasons to use asynchronous serial. For example, it’s still easier to connect a PC to a serial device (with a USB or RS-232 adapter) than to an I²C device. We expect to make more UART Motorons in the future, too.
|
|
|
Here is our full lineup of Motoron controllers to date, encompassing both the new “micro” boards and the previously-released expansion boards for Arduino and Raspberry Pi:
| Motoron motor controllers micro versions |
||
 M2T256 |
 M2U256 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Control interface: | I²C | UART serial |
| Motor channels: | 2 (dual) | |
| Absolute max input voltage: |
48 V | |
| Recommended max nominal battery voltage: |
36 V | |
| Max continuous current per channel: |
1.8 A | |
| Available versions: | ||
| Motoron motor controllers Arduino and Raspberry Pi form factor versions |
|||||
 M3S256  M3H256 |
 M2S24v14  M2H24v14 |
 M2S24v16  M2H24v16 |
 M2S18v18  M2H18v18 |
 M2S18v20  M2H18v20 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control interface: | I²C | ||||
| Motor channels: | 3 (triple) | 2 (dual) | |||
| Absolute max input voltage: |
48 V | 40 V | 30 V | ||
| Recommended max nominal battery voltage: |
36 V | 28 V | 18 V | ||
| Max continuous current per channel: |
2 A | 14 A | 16 A | 18 A | 20 A |
| Available versions for Arduino: |
M3S256 | M2S24v14 | M2S24v16 | M2S18v18 | M2S18v20 |
| Available versions for Raspberry Pi: |
M3H256 | M2H24v14 | M2H24v16 | M2H18v18 | M2H18v20 |