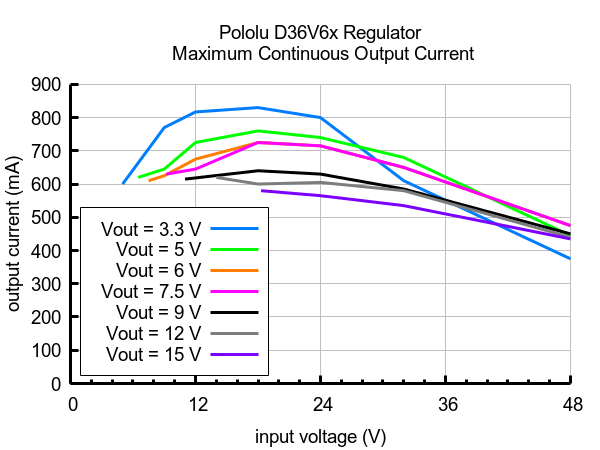
The D36V6x family of 600 mA buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 50 V. They are switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters), which makes them much more efficient than linear voltage regulators, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large. The maximum achievable output current of these regulators varies with the input voltage but also depends on other factors, including the ambient temperature, air flow, and heat sinking. The graph below shows maximum output currents that these regulators can deliver continuously at room temperature in still air and without additional heat sinking.
The regulators feature short-circuit/over-current protection, and thermal shutdown helps prevent damage from overheating. The boards do not have reverse-voltage protection, but reverse-voltage protection modules are available for adding that functionality.
| Regulator |
Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Size |
Special features |
Price |
| #3791: D36V6F3 |
3.3 V |
600 mA |
4 V – 50 V |
0.4″ × 0.5″ |
Short-circuit/over-current protection,
thermal shutdown |
$5.95 |
| #3792: D36V6F5 |
5 V |
5.2 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3793: D36V6F6 |
6 V |
6.2 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3794: D36V6F7 |
7.5 V |
7.7 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3795: D36V6F9 |
9 V |
9.2 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3796: D36V6F12 |
12 V |
12.2 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3797: D36V6F15 |
15 V |
15.2 V – 50 V |
$5.95 |
| #3798: D36V6ALV |
2.5 V – 7.5 V |
4 V – 50 V |
0.4″ × 0.6″ |
$7.95 |
| #3799: D36V6AHV |
4 V – 25 V |
$7.95 |
| Note 1: Actual achievable continuous current is a function of input and output voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information. |
| Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information. |
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “D36V6x Step-Down Voltage Regulators”
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 3.3 V |
600 mA |
4 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 5 V |
600 mA |
5.2 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 6 V |
600 mA |
6.2 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 7.5 V |
600 mA |
7.7 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 9 V |
600 mA |
9.2 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 12 V |
600 mA |
12.2 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 15 V |
600 mA |
15.2 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 2.5 V – 7.5 V |
600 mA |
4 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of the input and output voltage and limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 4 V – 25 V |
600 mA |
4 V – 50 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of the input and output voltage and limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category