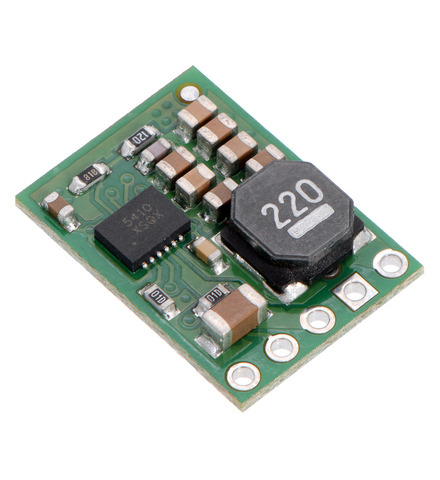
The D24V10Fx family of step-down voltage regulators features the Intersil ISL85410 1A synchronous buck regulator and generates lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 36 V. They are switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters) with typical efficiencies between 80% and 95%, which is much more efficient than linear voltage regulators, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large. These regulators have a power-save mode that activates at light loads and a low quiescent (no load) current draw, which make them well suited for applications that are run from a battery.
The regulators feature short-circuit/over-current protection, and thermal shutdown helps prevent damage from overheating. The boards do not have reverse-voltage protection.
| Regulator |
Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Size |
Special features |
Price |
| #2830: D24V10F3 |
3.3 V |
1 A |
3.4 V – 36 V |
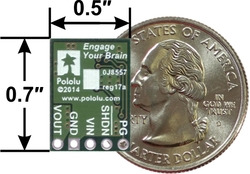
0.5″ × 0.7″ |
Short-circuit protection,
over-current protection,
thermal shutdown |
$11.95 |
| #2831: D24V10F5 |
5 V |
5.1 V – 36 V |
$11.95 |
| #2832: D24V10F6 |
6 V |
6.1 V – 36 V |
$11.95 |
| #2833: D24V10F9 |
9 V |
9.1 V – 36 V |
$11.95 |
| #2834: D24V10F12 |
12 V |
12.1 V – 36 V |
$11.95 |
| Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information. |
| Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information. |
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “D24V10Fx Step-Down Voltage Regulators”
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 3.3 V |
1 A |
3.4 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 5 V |
1 A |
5.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 6 V |
1 A |
6.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 9 V |
1 A |
9.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 12 V |
1 A |
12.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Typical continuous output current at 24 V in. Actual achievable continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. See the output current graphs on the product pages for more information.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category











