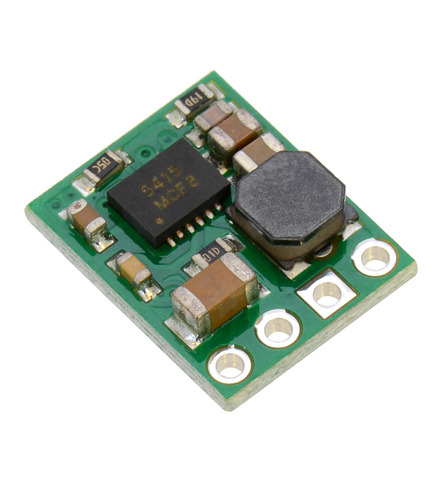
The D24V5x family of 500 mA synchronous buck (step-down) voltage regulators generates lower output voltages from input voltages as high as 36 V. They are switching regulators (also called switched-mode power supplies (SMPS) or DC-to-DC converters), which makes them much more efficient than linear voltage regulators, especially when the difference between the input and output voltage is large. These regulators have very low drop-out voltages.
The regulators feature short-circuit/over-current protection, and thermal shutdown helps prevent damage from overheating. The boards do not have reverse-voltage protection.
| Regulator |
Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
Size |
Special features |
Price |
| #2840: D24V5F1 |
1.8 V |
500 mA |
3 V – 36 V |
0.4″ × 0.5″ |
Short-circuit protection,
over-current protection,
thermal shutdown |
$8.95 |
| #2841: D24V5F2 |
2.5 V |
3 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2842: D24V5F3 |
3.3 V |
3.4 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2843: D24V5F5 |
5 V |
5.1 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2844: D24V5F6 |
6 V |
6.1 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2845: D24V5F9 |
9 V |
9.1 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2846: D24V5F12 |
12 V |
12.1 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| #2847: D24V5F15 |
15 V |
15.1 V – 36 V |
$8.95 |
| Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input and output voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. |
| Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information. |
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “D24V5Fx Step-Down Voltage Regulators”
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 1.8 V |
500 mA |
3 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 2.5 V |
500 mA |
3 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 3.3 V |
500 mA |
3.4 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 5 V |
500 mA |
5.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 6 V |
500 mA |
6.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 9 V |
500 mA |
9.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 12 V |
500 mA |
12.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
| Output voltage |
Typical max output current1 |
Input voltage range2 |
| 15 V |
500 mA |
15.1 V – 36 V |
Note 1: Actual achievable maximum continuous output current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
Note 2: Minimum input voltage is subject to dropout voltage considerations; see the dropout voltage section of product pages for more information.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category