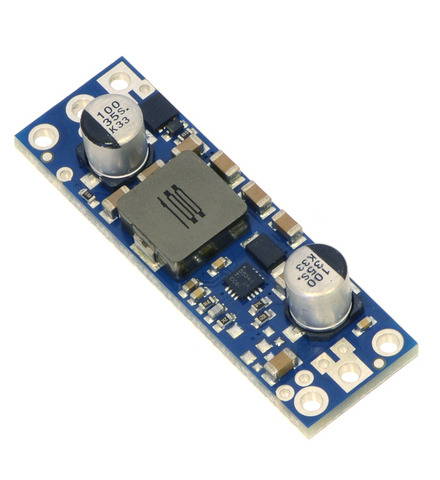
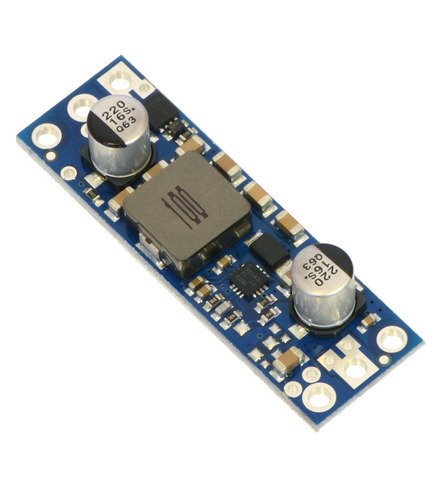
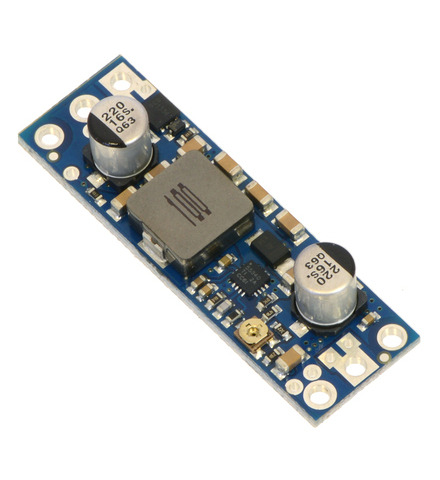
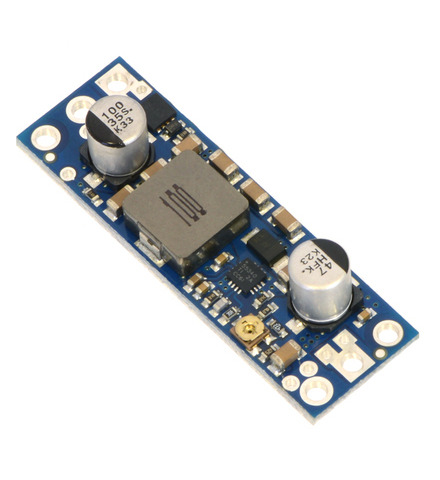
Note: We recommend our newer U3V70x family of boost regulators over these older U3V50x regulators for applications that require 20 V or less. The U3V70x regulators are smaller and can deliver more current, and the adjustable version features a precision 12-turn potentiometer, which makes it easier to set the output voltage to a particular value.
This family of boost regulators can generate up to 30 V from input voltages as low as 2.9 V while allowing for input currents as high as 5 A and offering typical efficiencies of 80% to 95%. The regulators include built-in reverse-voltage protection, over-current protection, thermal shutdown, and an under-voltage lockout that keeps the modules from behaving erratically when the input voltage gets too low. The U3V50x family includes versions with fixed 5 V, 6 V, 9 V, 12 V, or 24 V outputs and versions with adjustable 4 V to 12 V or 9 V to 30 V outputs:
| Regulator |
Output voltage |
Typical input current* |
Min input voltage |
Size |
Special features |
Price |
| #2565: U3V50F5 |
5 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
0.6″ × 1.9″ |
Reverse-voltage protection,
over-current protection,
over-temperature shutoff,
under-voltage lockout |
$29.95 |
| #2566: U3V50F6 |
6 V |
$29.95 |
| #2567: U3V50F9 |
9 V |
$29.95 |
| #2568: U3V50F12 |
12 V |
$29.95 |
| #2569: U3V50F24 |
24 V |
$31.95 |
| #2570: U3V50ALV |
4 V – 12 V |
$29.95 |
| #2571: U3V50AHV |
9 V – 30 V |
$33.95 |
| *Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input and output voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation. |
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category
Products in category “U3V50x Step-Up Voltage Regulators”
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 5 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 6 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 9 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 12 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 24 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 4 V – 12 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
| Output voltage |
Typical max input current* |
Min input voltage |
| 9 V – 30 V |
5 A |
2.9 V |
*Actual achievable maximum continuous current is a function of input voltage and is limited by thermal dissipation.
 Compare all products in this category
Compare all products in this category