
This is a merged information page for Item #3416.
View normal product page.
Pololu item #:
3416
Brand:
Pololu
Status:
Active and Preferred

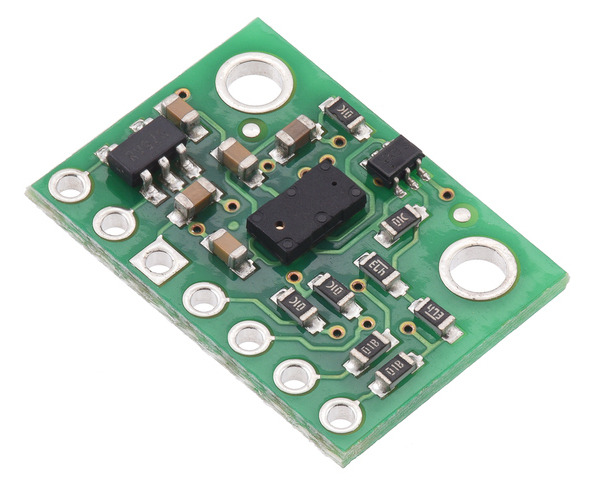
This sensor is a carrier/breakout board for ST’s VL53L3CX laser-ranging sensor, which offers fast and accurate ranging up to 5 m. It uses the time of flight (ToF) of invisible, eye-safe laser pulses to measure absolute distances to multiple targets simultaneously, independent of ambient lighting conditions and target characteristics like color, shape, and texture (though these things will affect the maximum range). Distance measurements can be read through a digital I²C interface. The board includes a 2.8 V linear regulator and level-shifters that allow it to work over an input voltage range of 2.6 V to 5.5 V, and the 0.1″ pin spacing makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1″ perfboards. Note: This is not recommended for use with 8-bit MCUs; for such applications, consider the VL53L1X, VL53L0X carrier, or VL6180X carrier.
 Compare all products in Carriers for ST Time-of-Flight (ToF) Distance Sensors.
Compare all products in Carriers for ST Time-of-Flight (ToF) Distance Sensors.
 |
VL53L3CX Time-of-Flight Multi-Target Distance Sensor Carrier with Voltage Regulator, 300cm Max. |
|---|
 |
VL53L3CX Time-of-Flight Multi-Target Distance Sensor Carrier with included header pins. |
|---|
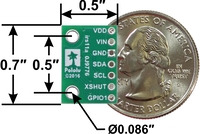 |
VL53L0X/VL53L1X/VL53L3CX/VL53L4CD Time-of-Flight Distance Sensor Carrier, bottom view with dimensions. |
|---|
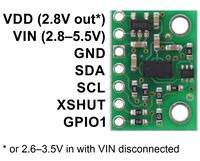 |
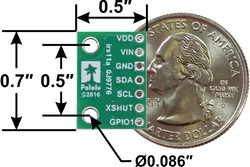
Pinout diagram of the VL53L3CX/VL53L4CD Time-of-Flight Multi-Target Distance Sensor Carrier. |
|---|
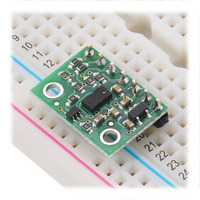 |
VL53L3CX Time-of-Flight Multi-Target Distance Sensor Carrier in a breadboard. |
|---|
 |
Schematic diagram of the VL53L0X/VL53L1X/VL53L3CX/VL53L4CD Time-of-Flight Distance Sensor Carrier. |
|---|
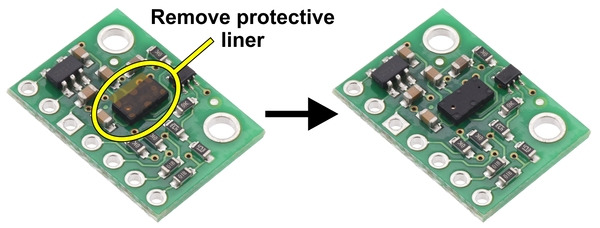
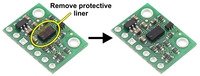 |
The VL53L3CX carrier might ship with a protective liner covering the sensor IC that must be removed before use. |
|---|
 |
Comparison of the VL6180X, VL53L4CD, VL53L0X, VL53L1X, VL53L3CX, VL53L5CX, VL53L7CX, and VL53L8CX Time-of-Flight Distance Sensor Carriers. |
|---|
 |
Standard packaging for the VL53L3CX Time-of-Flight Multi-Target Distance Sensor Carrier with Voltage Regulator, 300cm Max |
|---|
Note: This product is not recommended for use with 8-bit microcontrollers, and we also therefore do not provide support for it in the form of Arduino libraries as we do our other time-of-flight sensors. The VL53L3CX does not directly provide distance measurements. Instead, it provides histogram data that can be processed with algorithms provided by ST. This processing requires a significant amount of RAM and code space, making this sensor impractical for use with a typical 8-bit microcontroller. (For example, a program we compiled for an STM32F4 microcontroller that does little more than get readings from the VL53L3CX uses 63 KB of flash and 14 KB of global variables in RAM.) For alternatives that are simpler to use and can work with 8-bit microcontrollers, please consider the VL53L1X, VL53L0X carrier, or VL6180X carrier.
 |
The VL53L3CX from ST Microelectronics is a long-distance ranging time-of-flight (TOF) sensor integrated into a compact module. This board is a carrier for the VL53L3CX , so we recommend careful reading of the VL53L3CX datasheet (1MB pdf) before using this product.
The VL53L3CX is effectively a tiny, self-contained lidar system featuring an integrated 940 nm Class 1 laser, which is invisible and eye-safe. Unlike conventional IR sensors that use the intensity of reflected light to estimate the distance to an object, the VL53L3CX uses ST’s FlightSense technology to precisely measure how long it takes for emitted pulses of infrared laser light to reach the objects and be reflected back to a detector. This approach ensures absolute distance measurements independent of ambient lighting conditions and target characteristics (e.g. color, shape, texture, and reflectivity), though these external conditions do affect the maximum range of the sensor.
Under favorable conditions, the sensor can report distances up to 5 m (16 ft) with 1 mm resolution. The minimum ranging distance is 10 mm. Ranging measurements are available through the sensor’s I²C (TWI) interface, which is also used to configure sensor settings, and the sensor provides two additional pins: a shutdown input and an interrupt output.
The VL53L3CX is a great IC, but its small, leadless, LGA package makes it difficult for the typical student or hobbyist to use. It also operates at a recommended voltage of 2.8 V, which can make interfacing difficult for microcontrollers operating at 3.3 V or 5 V. Our breakout board addresses these issues, making it easier to get started using the sensor, while keeping the overall size as small as possible.
The carrier board includes a low-dropout linear voltage regulator that provides the 2.8 V required by the VL53L3CX and allows the sensor to be powered from a 2.6 V to 5.5 V supply. The regulator output is available on the VDD pin and can supply around 100 mA to external devices. The breakout board also includes a circuit that shifts the I²C clock and data lines to the same logic voltage level as the supplied VIN, making it simple to interface the board with 3.3 V or 5 V systems, and the board’s 0.1″ pin spacing makes it easy to use with standard solderless breadboards and 0.1″ perfboards. The board ships fully populated with its SMD components, including the VL53L3CX, as shown in the product picture.
The VL53L0X, VL53L1X, VL53L3CX, and VL53L4CD carriers all use the same PCB (labeled irs11a) and look similar (although the VL53L1X’s gold-colored windows make it easy to distinguish from the others):
|
|
|
|
You can refer to the pictures above to help differentiate them, and you might also consider marking your boards if you have multiple types of these sensors.
For other similar sensors, see the comparison section at the bottom of this page.
A 1×7 strip of 0.1″ header pins and a 1×7 strip of 0.1″ right-angle header pins are included, as shown in the picture below. You can solder the header strip of your choice to the board for use with custom cables or solderless breadboards, or you can solder wires directly to the board itself for more compact installations.
|
|
The board has two mounting holes spaced 0.5″ apart that work with #2 and M2 screws (not included).
Important note: This product might ship with a protective liner covering the sensor IC. The liner must be removed for proper sensing performance.
 |
 |
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VDD | Regulated 2.8 V output. Up to around 100 mA is available to power external components. (If you want to bypass the internal regulator, you can instead use this pin as an input for voltages between 2.6 V and 3.5 V with VIN disconnected.) |
| VIN | This is the main 2.8 V to 5.5 V power supply connection. The SCL and SDA level shifters pull the I²C lines high to this level. |
| GND | The ground (0 V) connection for your power supply. Your I²C control source must also share a common ground with this board. |
| SDA | Level-shifted I²C data line: HIGH is VIN, LOW is 0 V |
| SCL | Level-shifted I²C clock line: HIGH is VIN, LOW is 0 V |
| XSHUT | This pin is an active-low shutdown input; the board pulls it up to VDD to enable the sensor by default. Driving this pin low puts the sensor into hardware standby. This input is not level-shifted and it is not 5V-tolerant. |
| GPIO1 | Programmable interrupt output (VDD logic level). This output is not level-shifted. |
At least four connections are necessary to use the VL53L3CX board: VIN, GND, SCL, and SDA. The VIN pin should be connected to a 2.8 V to 5.5 V source, and GND should be connected to 0 volts. An on-board linear voltage regulator converts VIN to a 2.8 V supply, which can be accessed via the VDD pin, for the VL53L3CX IC. Supply voltages between 2.6 V and 3.5 V can also be connected to VDD (with VIN left disconnected) to bypass the regulator and power the board directly.
The I²C pins, SCL and SDA, are connected to built-in level-shifters that make them safe to use at voltages above VDD; they should be connected to an I²C bus operating at the same logic level as VIN (or VDD, if powering the board through VDD).
The XSHUT pin is an input and the GPIO1 pin is an open-drain output; both pins are pulled up to VDD by the board. They are not connected to level-shifters on the board and are not 5V-tolerant, but they are usable as-is with many 3.3 V and 5 V microcontrollers: the microcontroller can read the GPIO1 output as long as its logic high threshold is below VDD, and the microcontroller can alternate its own output between low and high-impedance states to drive the XSHUT pin. Alternatively, our 4-channel bidirectional logic level shifter can be used externally with those pins.
 |
The above schematic shows the additional components the carrier board incorporates to make the VL53L3CX easier to use, including the voltage regulator that allows the board to be powered from a 2.6 V to 5.5 V supply and the level-shifter circuit that allows for I²C communication at the same logic voltage level as VIN. This schematic is also available as a downloadable PDF (96k pdf).
The VL53L3CX can be configured and its distance readings can be queried through the I²C bus. Level shifters on the I²C clock (SCL) and data (SDA) lines enable I²C communication with microcontrollers operating at the same voltage as VIN (2.6 V to 5.5 V). A detailed explanation of the I²C interface on the VL53L3CX can be found in its datasheet, and more detailed information about I²C in general can be found in NXP’s I²C-bus specification (1MB pdf).
The sensor’s 7-bit slave address defaults to 0101001b on power-up. It can be changed to another value by writing one of the device configuration registers, but the new address only applies until the sensor is reset or powered off. ST provides an application note (196k pdf) that describes how to use multiple VL53L0X sensors on the same I²C bus by individually bringing each sensor out of reset and assigning it a unique address, and the approach can be easily adapted to apply to the VL53L3CX instead.
The I²C interface on the VL53L3CX is compliant with the I²C Fast-mode Plus (1 MHz) standard.
In contrast with the information available for many other devices, ST has not publicly released a register map and descriptions or other documentation about configuring and controlling the VL53L3CX. Instead, communication with the sensor is intended to be done through ST’s VL53L3CX API (STSW-IMG015), a set of C functions that take care of the low-level interfacing. To use the VL53L3CX, you can customize the API to run on a host platform of your choice using the information in the API documentation. Alternatively, it is possible to use the API source code as a guide for your own implementation.
ST also provides an alternative VL53L3CX ultra-low power (ULP) API (STSW-IMG033), which configures the sensor as a basic proximity detector with very low current consumption (less than 100 μA in some cases). In this mode, the sensor does not output distance and other data as usual; it simply raises an interrupt when a target is detected. The ULP and standard drivers can be used together to make the VL53L3CX act as a low-power proximity detector, then turn into an accurate ranging sensor once it sees a target.
We make pin-compatible carriers/breakout boards for several different ST time-of-flight (ToF) ranging sensors, as shown in the table below. They all function as tiny lidar systems featuring an integrated 940 nm Class 1 (i.e. invisible and eye-safe) laser, and they are all based on the same FlightSense technology, which precisely measures how long it takes for emitted pulses of infrared laser light to reach the objects and be reflected back to a detector. This approach ensures absolute distance measurements independent of ambient lighting conditions and target characteristics (e.g. color, shape, texture, and reflectivity), though these external conditions do affect the maximum range of the sensor. These sensors are all capable of 1 mm resolution, with some limitations on some versions.
 VL6180X carrier |
 VL53L4CD carrier |
 VL53L0X carrier |
 VL53L1X carrier |
 VL53L3CX carrier |
 VL53L5CX carrier |
 VL53L7CX carrier |
 VL53L8CX carrier |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum range:(1) | 60 cm | 120 cm | 200 cm | 400 cm | 500 cm | 400 cm | 350 cm | 400 cm |
| Minimum range: | ~10 mm | 1 mm | ~30 mm | 40 mm | 10 mm | 20 mm | ||
| Field of view: | 25° | 18° | 25° | 15° to 27° diagonal, programmable |
25° | 65° diagonal, up to 8×8 zones |
90° diagonal, up to 8×8 zones |
65° diagonal, up to 8×8 zones |
| Other features: | ambient light sensing, low memory footprint(2) |
low memory footprint(2), ultra-low power mode |
low memory footprint(2) | low memory footprint(2), ultra-low power mode |
multi-target detection, ultra-low power mode |
multi-target detection | multi-target detection | multi-target detection, improved performance in ambient light |
| Maximum update rate:(1) | ~150 Hz | 100 Hz | 50 Hz | 100 Hz | 125 Hz | 60 Hz | ||
| Operating voltage range: | 2.6 V to 5.5 V | 2.5 V to 5.5 V | 3.2 V to 5.5 V | |||||
| Regulator voltage: | 2.8 V | 3.3 V | 1.8 V and 3.3 V | |||||
| Typical active-ranging supply current: |
25 mA | 25 mA | 20 mA | 20 mA | 20 mA | 100 mA | ||
| Peak supply current: | 40 mA | 150 mA | ||||||
| Interface: | I²C | I²C, SPI | ||||||
| Dimensions: | 0.5″ × 0.7″ | 0.5″ × 0.9″ | ||||||
| 1-piece price: | $13.49 | $12.95 | $14.95 | $18.95 | $16.95 | $19.95 | $19.95 | $24.95 |
| 1 Effective range and update rate depend on configuration, target, and environment. 2 Suitable for use with typical 8-bit MCUs. |
||||||||
Most of these carriers have the same physical dimensions (0.5″ × 0.7″) and work in 3.3 – 5 V systems (thanks to their integrated linear regulators and level-shifters), and they can all be controlled through an I²C interface. However, they have different APIs and memory requirements, so software will generally need to be rewritten when switching between sensors in an application, and versions with higher memory requirements are generally not suitable for use with typical 8-bit microcontrollers.
| Size: | 0.5″ × 0.7″ × 0.085″1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 0.5 g1 |
| Resolution: | 1 mm |
|---|---|
| Maximum range: | 500 cm2 |
| Minimum range: | 1 cm |
| Interface: | I²C |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 2.6 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Supply current: | 20 mA3 |
| PCB dev codes: | irs11a |
|---|---|
| Other markings: | 0J9776 |
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes.
This application note from ST describes how to use multiple VL53L0X sensors on a single I²C bus.
The official specification for the I²C-bus, which is maintained by NXP.
ST’s product page for the VL53L3CX time-of-flight ranging sensor IC, with links to its most up-to-date datasheet, software, and other resources.
ST’s API (application programming interface) for the VL53L3CX.
ST’s Ultra-Low Power API (application programming interface) for the VL53L3CX, which allows it to operate as a proximity detector with very low current consumption.
No FAQs available.
December 2020 update: ST originally specified a 3 m (10 ft) maximum range for the VL53L3CX, and we initially released this product with the name...