
This is a merged information page for Item #2980.
View normal product page.
Pololu item #:
2980
Brand:
Pololu
Status:
Active and Preferred

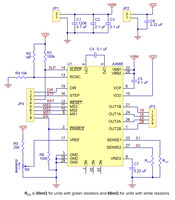
This version of our A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier ships with male header pins installed, so no soldering is required to use it with an appropriate 16-pin socket or solderless breadboard. Please see the A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier product page for more information about the driver.
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): header pins soldered? bulk packaged? Select variant…
 Compare all products in A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carriers or
Compare all products in A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carriers or  16-pin Stepper Motor Drivers.
16-pin Stepper Motor Drivers.
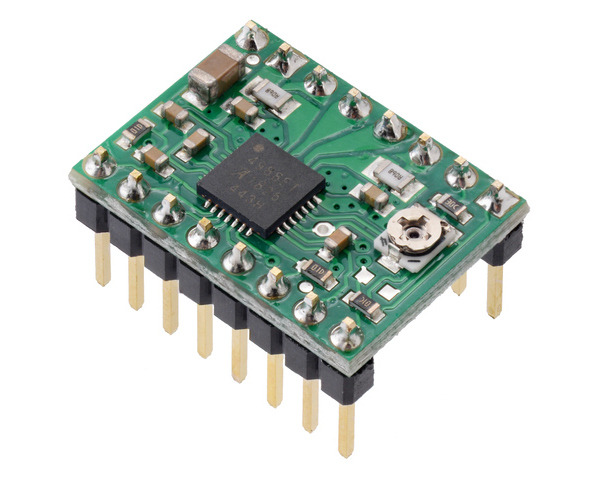
 |
Schematic diagram of the A4988 stepper motor driver carrier (both green and black editions). |
|---|
 |
Pololu A4988 stepper motor driver carrier with included header pins soldered. |
|---|
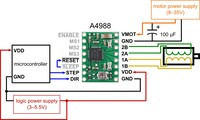 |
Minimal wiring diagram for connecting a microcontroller to an A4988 stepper motor driver carrier (full-step mode). |
|---|
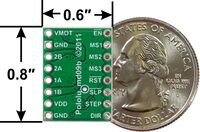 |
A4983/A4988 stepper motor driver carrier with dimensions. |
|---|
This version of our A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier ships with 0.1″-pitch male header pins installed as shown in the main product picture, so no soldering is required to use it with an appropriate 16-pin socket or solderless breadboard. Please see the A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier product page for more information about the driver.
| Size: | 0.6″ × 0.8″ |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 2.4 g |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 8 V |
|---|---|
| Maximum operating voltage: | 35 V |
| Continuous current per phase: | 1 A1 |
| Maximum current per phase: | 2 A2 |
| Minimum logic voltage: | 3 V |
| Maximum logic voltage: | 5.5 V |
| Microstep resolutions: | full, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, and 1/16 |
| Reverse voltage protection?: | N |
| Bulk packaged?: | N |
| Header pins soldered?: | Y |
| PCB dev codes: | md09b |
|---|
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes. It applies to both the green (md09b) and black (md09c) editions of the A4988 stepper motor driver carrier.
A short video showing the in-house assembly of a panel of Black Edition A4988 stepper motor driver carriers on our Samsung SM421F pick and place machine.
A customer-made module for using the Pololu A4983/A4988 Stepper Motor Driver Carrier in Kicad. By Jared Harvey, October 2011.
Yes. To avoid damaging your stepper motor, you want to avoid exceeding the rated current, which is 600 mA in this instance. All of our stepper motor drivers let you limit the maximum current, so as long as you set the limit below the rated current, you will be within spec for your motor, even if the voltage exceeds the rated voltage. The voltage rating is just the voltage at which each coil draws the rated current, so the coils of your stepper motor will draw 600 mA at 3.9 V. By using a higher voltage along with active current limiting, the current is able to ramp up faster, which lets you achieve higher step rates than you could using the rated voltage.
If you do want to use a lower motor supply voltage for other reasons, consider using our DRV8834 or STSPIN-220 low-voltage stepper motor drivers.
Yes, you do! Setting the current limit on your stepper motor driver carrier before connecting your motor is essential to making sure that it runs properly. An appropriate current limit also ensures that your motor is not allowed to draw more current than it or your driver can handle, since that is likely to damage one or both of them.
Setting the current limit on our A4988, DRV8825, DRV8824, DRV8834, DRV8880, STSPINx20, and TB67SxFTG stepper motor driver carriers is done by adjusting the on-board potentiometer. We strongly recommend using a multimeter to measure the VREF voltage while setting the current limit so you can be sure you set it to an appropriate value (just turning the pot randomly until things seem to work is not a good approach). The following video has more details on setting the current limit:
Measuring the current draw at the power supply does not necessarily provide an accurate measure of the coil current. Since the input voltage to the driver can be significantly higher than the coil voltage, the measured current on the power supply can be quite a bit lower than the coil current (the driver and coil basically act like a switching step-down power supply). Also, if the supply voltage is very high compared to what the motor needs to achieve the set current, the duty cycle will be very low, which also leads to significant differences between average and RMS currents: RMS current is what is relevant for power dissipation in the chip but many power supplies won’t show that. You should base your assessment of the coil current on the set current limit or by measuring the actual coil currents.
Please note that while the A4988 driver IC is capable of supplying 2 A per coil, the chip by itself will overheat at lower currents. The carrier board PCB helps draw heat away from the IC, but we have found that it generally requires a heat sink to deliver more than approximately 1 A per coil (the Black Edition A4988 carrier has a four-layer PCB that lets it deliver up to around 1.2 A per coil without a heat sink), but this number depends on factors such as ambient temperature and air flow. For example, sealing three A4988 driver carriers in close proximity in a small box will cause them to overheat at lower currents than a unit by itself in open air.
We recently substantially reduced prices on our stepper motor driver carriers, and I figured this announcement was a good time to give you an update...