
This is a merged information page for Item #2465.
View normal product page.
Pololu item #:
2465
Brand:
Pololu
Status:
Obsolete

This small digital distance sensor detects objects between 0.5 cm and 15 cm (0.2″ and 6″) away. With its quick response time, small size, low current draw, and short minimum sensing distance, this sensor is a good choice for non-contact, close-proximity object detection, and our compact carrier PCB makes it easy to integrate into your project.
Alternatives available with variations in these parameter(s): maximum range Select variant…
 |
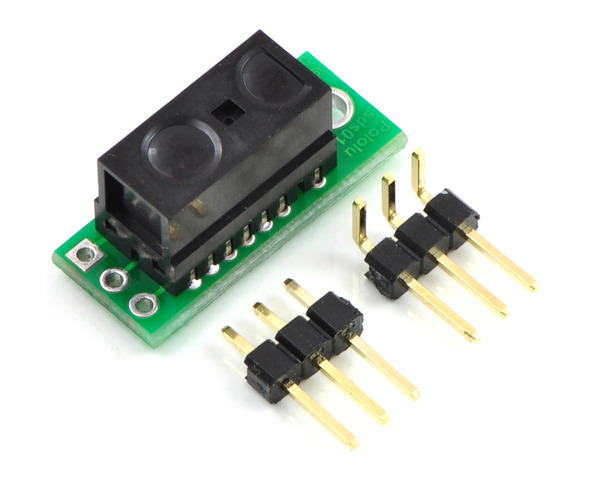
Pololu carrier with Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, or GP2Y0D815Z0F digital distance sensor. |
|---|
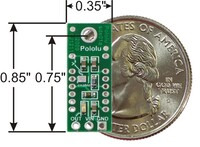 |
Pololu carrier for Sharp GP2Y0D815Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, and GP2Y0D805Z0F with quarter for size reference. |
|---|
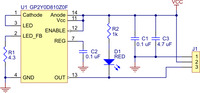 |
Pololu carrier for Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, and GP2Y0D815Z0F sensors schematic diagram. |
|---|
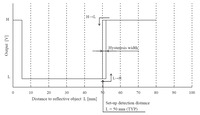 |
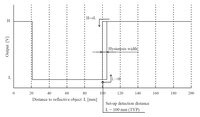
Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F digital distance sensor 5 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
 |
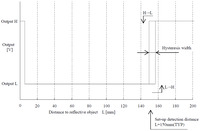
Sharp GP2Y0D810Z0F digital distance sensor 10 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
 |
Sharp GP2Y0D815Z0F digital distance sensor 15 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
 |
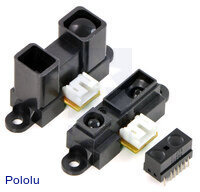
Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, or GP2Y0D815Z0F digital distance sensor. |
|---|
 |
A variety of Sharp distance sensors. |
|---|
 |
These sensors are a great way to quickly detect the presence of nearby objects. It consists of a Sharp GP2Y0D805, GP2Y0D810, or GP2Y0D815 sensor module installed on our tiny carrier board for these sensors, which includes all of the external components required to make them work. The available versions offer three different sensing ranges:
There are a few millimeters of hysteresis around the maximum range threshold and no hysteresis at the minimum range threshold. Note that these sensors will only tell you if there is an object within the detection range along their narrow lines of sight; they will not tell you how far away the object is.
With detection distances up to 150 mm and a typical sampling rate of almost 400 Hz, these sensors provides an attractive alternative to shorter-range LED-phototransistor reflectance pairs and longer-range but slower sensors such as the Sharp GP2Y0A41SK0F analog distance sensor. The output, Vo, is driven low when the sensor detects an object; otherwise, the output is high.
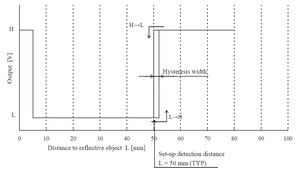 |
Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F digital distance sensor 5 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
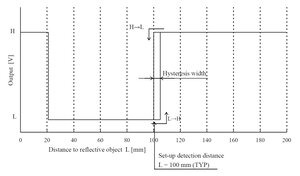 |
Sharp GP2Y0D810Z0F digital distance sensor 10 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
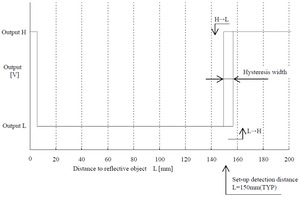 |
Sharp GP2Y0D815Z0F digital distance sensor 15 cm measuring characteristics. |
|---|
Some example applications include:
The Pololu carrier board lets you interface with the GP2Y0D805, GP2Y0D810, or GP2Y0D815 sensor using a three-pin 0.1″ connector, such as the included 3×1 straight male header strip and 3×1 right-angle male header strip. You can connect to these pins with a servo cable or with a custom-made cable using pre-crimped wires and a 3×1 crimp connector housing.
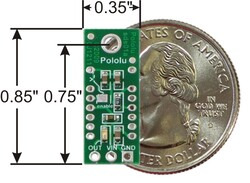
The square pad is ground, the middle pad is VIN (2.7 – 6.2 V), and the remaining pad is the sensor output, OUT. Depending on your power source, you might notice an increase in performance by placing a large (>10 uF) capacitor between power and ground somewhere near the sensor.
A red LED on the back of the PCB lights when the output is low, indicating that the sensor is detecting something. With the LED in the circuit, the low output signal will be around 1 V. If so desired, you can disable this LED by cutting the trace between it and the OUT pin where it is marked on the silkscreen or by desoldering the LED, in which case the low voltage will be below 0.6 V.
The GP2Y0D805, GP2Y0D810, and GP2Y0D815 have an optional enable input that can be used to put the sensor into low-power mode. The Pololu carrier board connects this input to Vcc so that the sensor is always enabled, but you can solder a wire to the pad labeled “enable” on the back of the PCB if you want control over this input. Note that you will need to cut the trace that connects the enable line to Vcc on the PCB if you want to be able to disable the sensor. This trace is marked on the silkscreen, and there is a caret that indicates where we suggest you make the cut.
The carrier board has a 0.086″ mounting hole for a #2 or M2 screw. You can make the module more compact by cutting or grinding off this portion of the PCB if you do not need the mounting hole.
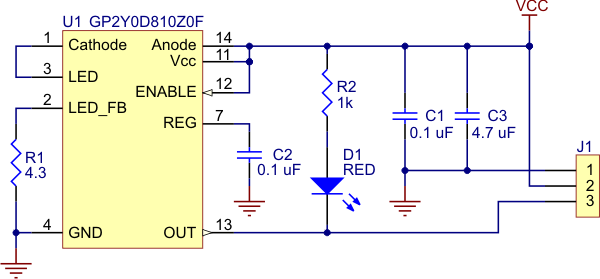 |
Pololu carrier for Sharp GP2Y0D805Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, and GP2Y0D815Z0F sensors schematic diagram. |
|---|
These carrier boards are based on sensors from Sharp/Socle that are no longer in production, so we do not recommend them for new designs where continued availability is important. As an alternative, consider the newer Pololu Digital Distance Sensors, which have the same form factor and pinout as this board.
The Pololu distance sensors are available in the same 5 cm, 10 cm, and 15 cm ranges as the Sharp sensors, in addition to longer ranges of up to several meters. This means they can be used as replacements for these older modules, and the longer-range versions can serve as upgrades that provide enhanced detection and measurement capabilities. Also available are versions with pulse-width outputs that can provide quantitative distance measurements instead of simply indicating the presence of an object.
The sensors on these newer units are much thinner than the Sharp modules, so the zero-range point is approximately 7 mm closer to the PCB, and the beam angle of the newer units is wider. The pictures below show side-by-side comparisons of the two:
|
|
|
We carry several analog Sharp distance sensors as well: the Sharp GP2Y0A51SK0F 2 – 15 cm, the Sharp GP2Y0A41SK0F 4 – 30 cm, the Sharp GP2Y0A21YK0F 10 – 80 cm, and the Sharp GP2Y0A02YK0F 20 – 150 cm. These analog distance sensors have longer minimum detection distances and much slower response times than the GP2Y0D805, GP2Y0D810, and GP2Y0D815, but they can see farther and report the distance to the detected object rather than simply if an object is detected.
 |
A variety of Sharp distance sensors. From left to right: GP2Y0A02, GP2Y0A21 or GP2Y0A41, GP2Y0A51, and GP2Y0D8xx. |
|---|
We also carry the newer Sharp GP2Y0A60SZ analog distance sensor (10 – 150 cm), which outperforms the other analog Sharp distance sensors in almost all respects, offering a low minimum detection distance, high maximum detection distance, wide 3 V output voltage differential, high 60 Hz sampling rate, operation down to 2.7 V, and optional enable control, all in a smaller package.
 |
Sharp GP2Y0A02YK0F Sensor 20-150cm (left) next to Pololu Carrier with Sharp GP2Y0A60SZLF Sensor 10-150cm (right). |
|---|
Note: This product comes with the GP2Y0D805Z0F, GP2Y0D810Z0F, or GP2Y0D815Z0F soldered into the carrier PCB. We sell the sensor modules by themselves, and we sell the carrier PCB without the sensor for those who already have the sensor or who want to solder the board together personally.
| Size: | 0.85″ × 0.35″ × 0.41″1 |
|---|---|
| Weight: | 1.4 g1 |
| Maximum range: | 15 cm |
|---|---|
| Minimum range: | 0.5 cm |
| Sampling rate: | 390 Hz2 |
| Minimum operating voltage: | 2.7 V |
| Maximum operating voltage: | 6.2 V |
| Supply current: | 5 mA3 |
| Output type: | digital4 |
Datasheet for the GP2Y0D815 15cm Sharp digital distance sensor.
Datasheet for the GP2Y0D810 10cm Sharp digital distance sensor.
Datasheet for the GP2Y0D805 5cm Sharp digital distance sensor.
This DXF drawing shows the locations of all of the board’s holes.
Sharp’s optical rangefinders and distance sensors have long been a favorite among robot builders for quick, easy, and affordable obstacle...