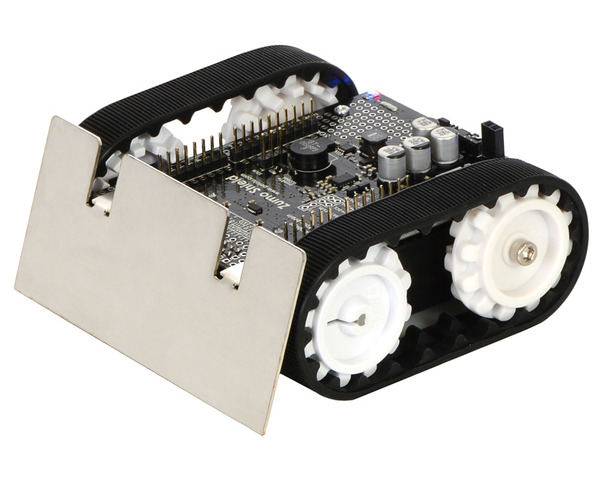
Zumo Robot for Arduino (Assembled with 75:1 HP Motors)
The Pololu Zumo robot is an Arduino-controllable tracked robot platform that is less than 10 cm × 10 cm—small enough to qualify for Mini Sumo. It includes two micro metal gearmotors coupled to a pair of silicone tracks, a stainless steel bulldozer-style blade, an array of six infrared reflectance sensors for line following or edge detection, a 3-axis accelerometer and magnetometer, and a buzzer for simple sounds and music. Just add 4 AA batteries and an Arduino (or compatible controller) and you are ready to push! No soldering or assembly is required.
| Description | Specs (2) | Pictures (6) | Resources (8) | FAQs (0) | On the blog (4) | Distributors (0) |
|---|
File downloads
-
Zumo Shield schematic diagrams (121k pdf)
-
Zumo Shield front expansion pinout (552k pdf)
Recommended links
-
Zumo Shield Libraries
This collection of libraries and examples for the Arduino that make it easy to program an Arduino-controlled robot built with Pololu’s Zumo Shield or Zumo robot kit (also available fully assembled).
-
LSM303 Arduino library
This is a library for the Arduino that interfaces with our LSM303D, LSM303DLHC, and LSM303DLM 3D compass and accelerometer carriers as well as the compass and accelerometer ICs on the MinIMU-9 v3 and AltIMU-10 v4 (it also works with older versions of those boards, some of which used the LSM303DLH and LSM303DLHC). It makes it simple to configure the device and read the raw accelerometer and magnetometer data, and it has a function for computing the tilt-compensated heading for those looking to use the LSM303 as a tilt-compensated compass.
-
Simulink Library for Zumo Robot
This library can be used to program an Arduino-controlled Zumo through MATLAB and Simulink. It provides driver blocks for all the sensors present on the Zumo Robot as well as example models showing their usage.
-
How to program a Zumo robot with Simulink
This tutorial on the Adafruit Learning System guides you through the process of programming a Zumo robot with Simulink.
-
Zumo robot tuning tips
This article was written by Professor Erich Styger for his class on embedded systems programming at the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts. It describes various ways to tweak the performance of a Zumo to be more competitive in a Mini Sumo competition. Note that his Zumos use a custom PCB rather than our Zumo shield for Arduino; our shield has a lot of capacitance in parallel with the batteries that generally prevents the “battery inertia” problem Erich describes.
-
Freedom Zumo Robot
This robot is uses our Zumo robot kit, 75:1 micro metal gearmotors, and a Zumo reflectance sensor array. Instead of an Arduino it uses a Freescale FRDM-KL25Z as the microcontroller board, and sample code is available for line following and maze solving. By Erich, March 2013.